Have you ever heard of the Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO)? 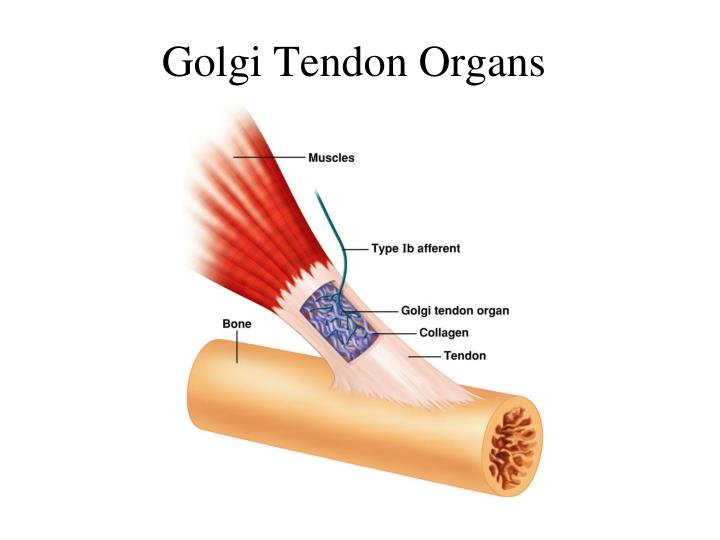
Read on to understand why full range of motion is crucial to weight resistance training and metabolism. The Golgi tendon organ (GTO) is a sensory receptor located in the tendons, near the point where they attach to the muscles. Its primary function is to monitor and regulate muscle tension.Understanding the Golgi tendon’s role is essential in the context of weight resistance training.
Function of the Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO) in Weight Resistance Training:
-
-
- Sensory Feedback: During weight resistance training, when a muscle contracts and exerts force to lift a weight, the muscle’s tension increases. This tension is detected by the Golgi tendon organ, which acts as a sensory feedback mechanism. The GTO measures the force generated by the muscle, as well as the stretching of the tendon due to that force.
- Inhibitory Response: When the Golgi tendon organ senses high levels of tension or force in the muscle-tendon complex, it triggers an inhibitory response. This response leads to the relaxation of the muscle undergoing contraction. Essentially, the GTO acts as a safety mechanism to prevent excessive force that could potentially cause muscle damage or injury.
- Protective Function: The GTO helps protect muscles from potential damage caused by overexertion. If the muscle contracts too forcefully or if the load is too heavy, the GTO inhibits the muscle’s contraction, reducing the force exerted on the tendon and muscle fibers.
- Autoregulation: The GTO plays a role in autoregulation during weight resistance training. It helps maintain a balance between muscle force generation and muscle protection. When the muscle force exceeds a safe threshold, the GTO reduces the muscle tension, preventing potential harm. On the other hand, when the load decreases or the muscle tension decreases, the GTO allows the muscle to generate more force.
-
How to Explain It to a Beginner in Weight Resistance Training:
To explain the Golgi tendon and its function in weight resistance training to a beginner, you can use simple language and real-life analogies:”Imagine the Golgi tendon organ as a smart sensor that sits near your muscles and tendons. When you lift weights or perform resistance exercises, your muscles work hard, generating force to lift those weights.
The Golgi tendon organ keeps an eye on how hard your muscles are working and the stress on your tendons.It’s like a safety guard for your muscles. When it senses that the force in your muscles is getting too high, it tells your brain to slow down a bit and relax the muscle. It does this to protect your muscles from getting injured. It’s a bit like how your knee-jerk reaction is to pull your hand away from something hot to avoid burning it.
So, during weight training, the Golgi tendon organ helps you find the right balance between pushing your muscles to get stronger and preventing them from overdoing it and getting hurt. It’s a clever mechanism that helps you train safely and effectively.”
Education Blog for Personal Trainers Education
By: Joe Antouri
PROPTA / Professional Personal Trainers Association
Worldwide Institute for Fitness & Nutrition for Education and Certification
¿Ha oído hablar alguna vez del órgano tendinoso de Golgi (OTG)? 
Siga leyendo para comprender por qué la amplitud de movimiento completa es crucial para el entrenamiento de resistencia con pesas y el metabolismo. El órgano tendinoso de Golgi (GTO) es un receptor sensorial situado en los tendones, cerca del punto donde se unen a los músculos. Su función principal es controlar y regular la tensión muscular, por lo que es esencial comprender el papel del tendón de Golgi en el contexto del entrenamiento de resistencia con pesas.
Función del órgano tendinoso de Golgi (OTG) en el entrenamiento de resistencia con pesas:
-
-
- Retroalimentación sensorial: Durante el entrenamiento de resistencia con pesas, cuando un músculo se contrae y ejerce fuerza para levantar un peso, la tensión del músculo aumenta. Esta tensión es detectada por el órgano tendinoso de Golgi, que actúa como mecanismo de retroalimentación sensorial. El GTO mide la fuerza generada por el músculo, así como el estiramiento del tendón debido a esa fuerza.
- Respuesta inhibitoria: Cuando el órgano tendinoso de Golgi detecta niveles elevados de tensión o fuerza en el complejo músculo-tendinoso, desencadena una respuesta inhibitoria. Esta respuesta conduce a la relajación del músculo en contracción. Esencialmente, el GTO actúa como un mecanismo de seguridad para evitar una fuerza excesiva que podría causar daños o lesiones musculares.
- Función protectora: El GTO ayuda a proteger los músculos de posibles daños causados por un esfuerzo excesivo. Si el músculo se contrae con demasiada fuerza o si la carga es demasiado pesada, el GTO inhibe la contracción del músculo, reduciendo la fuerza ejercida sobre el tendón y las fibras musculares.
- Autorregulación: El GTO desempeña un papel en la autorregulación durante el entrenamiento de resistencia con pesas. Ayuda a mantener un equilibrio entre la generación de fuerza muscular y la protección del músculo. Cuando la fuerza muscular supera un umbral de seguridad, el GTO reduce la tensión muscular, evitando posibles daños. Por otro lado, cuando la carga disminuye o la tensión muscular disminuye, el GTO permite que el músculo genere más fuerza.
-
Cómo explicárselo a un principiante en el entrenamiento de resistencia con pesas:
Para explicar el tendón de Golgi y su función en el entrenamiento de resistencia con pesas a un principiante, puede utilizar un lenguaje sencillo y analogías de la vida real: “Imagine el órgano tendinoso de Golgi como un sensor inteligente que se sitúa cerca de sus músculos y tendones. Cuando levanta pesas o realiza ejercicios de resistencia, sus músculos trabajan duro, generando fuerza para levantar esas pesas.
El órgano tendinoso de Golgi vigila el esfuerzo de los músculos y la tensión de los tendones, y es como un seguro para los músculos. Cuando detecta que la fuerza muscular es excesiva, le dice al cerebro que reduzca un poco la velocidad y relaje el músculo. Lo hace para evitar que los músculos se lesionen. Es algo parecido a la reacción instintiva de apartar la mano de algo caliente para evitar quemarse.
Así, durante el entrenamiento con pesas, el órgano tendinoso de Golgi te ayuda a encontrar el equilibrio adecuado entre forzar los músculos para que se fortalezcan y evitar que se excedan y se lesionen. Es un mecanismo inteligente que te ayuda a entrenar con seguridad y eficacia”.
Blog de educación para entrenadores personales Educación
Por: Joe Antouri
PROPTA / Asociación Profesional de Entrenadores Personales
Instituto Mundial de Fitness y Nutrición para la Educación y Certificación

