 Macronutrition Explained
Macronutrition Explained
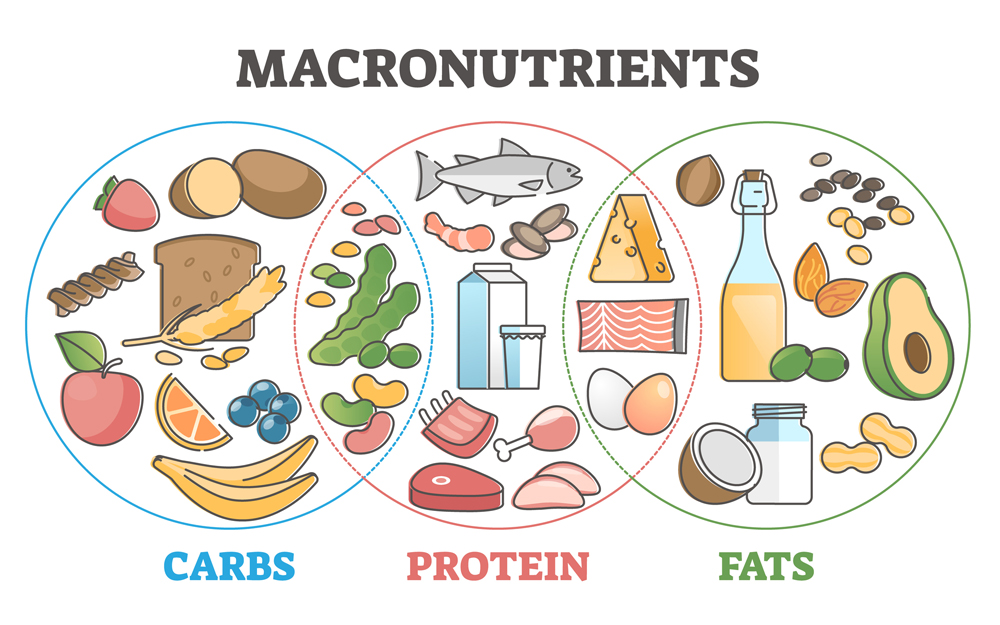
Macronutrition, also known as macronutrient nutrition, refers to the study and practice of managing the intake of major nutrients that the body requires in relatively larger amounts. These nutrients are essential for providing energy, building and repairing tissues, and supporting various physiological functions. The three main types of macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
-
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for the body. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by cells for fuel. Carbohydrates can be simple (sugars) or complex (starches and fiber). They are found in foods like grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, including muscles, skin, and internal organs. They are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Protein-rich foods include meat, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
- Fats: Fats provide energy, support cell structure, and help with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). There are different types of fats, including saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and trans fats. Healthy fats are found in sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Importance of Macronutrition: Balancing macronutrient intake is crucial for overall health and well-being. Each macronutrient plays specific roles in the body:
-
- Carbohydrates provide energy.
- Proteins build and repair tissues.
- Fats support cell function and provide long-lasting energy.
The proportions of these macronutrients in the diet can vary depending on factors such as age, activity level, health goals, and individual preferences.
Calculating Macronutrient Intake: Macronutrient needs vary from person to person. Calculating macronutrient intake often involves determining the optimal ratio of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats based on energy requirements and specific goals, such as weight management or muscle gain.
Balanced Diet: A balanced diet includes a variety of foods that provide the necessary macronutrients in appropriate proportions. The Dietary Guidelines recommend that carbohydrates make up about 45-65% of total daily calories, proteins around 10-35%, and fats around 20-35%.
Customization: Macronutrient needs can differ based on factors such as age, gender, metabolism, and activity level. Athletes might require more protein for muscle repair, while individuals focusing on weight loss might need to adjust their carbohydrate intake.
In summary, macronutrition is the practice of managing carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake to ensure that the body receives the necessary energy and nutrients for optimal functioning. Balancing these macronutrients plays a vital role in achieving and maintaining good health.
Education Blog for Personal Trainers Education Written by Joe Antouri / CEO PROPTA. All rights reserved.
WorldWide Institute for Fitness and Nutrition Education and Certification.
 Explicación de la macronutrición
Explicación de la macronutrición
La macronutrición, también conocida como nutrición de macronutrientes, se refiere al estudio y la práctica de gestionar la ingesta de los principales nutrientes que el cuerpo requiere en cantidades relativamente mayores. Estos nutrientes son esenciales para proporcionar energía, construir y reparar tejidos y respaldar diversas funciones fisiológicas. Los tres tipos principales de macronutrientes son los carbohidratos, las proteínas y las grasas.
-
- Carbohidratos: Los carbohidratos son una fuente primaria de energía para el cuerpo. Se descomponen en glucosa, que es utilizada por las células como combustible. Los carbohidratos pueden ser simples (azucares) o complejos (almidones y fibra). Se encuentran en alimentos como cereales, frutas, verduras y legumbres.
- Proteínas: Las proteínas son esenciales para construir y reparar tejidos, incluyendo músculos, piel y órganos internos. Están compuestas por aminoácidos, que son los bloques de construcción de las proteínas. Los alimentos ricos en proteínas incluyen carne, pescado, productos lácteos, legumbres y frutos secos.
- Grasas: Las grasas proporcionan energía, apoyan la estructura celular y ayudan en la absorción de las vitaminas liposolubles (A, D, E y K). Hay diferentes tipos de grasas, incluidas las grasas saturadas, insaturadas y trans. Las grasas saludables se encuentran en fuentes como aguacates, nueces, semillas y pescado graso.
Importancia de la Macronutrición: Equilibrar la ingesta de macronutrientes es crucial para la salud y el bienestar general. Cada macronutriente tiene roles específicos en el cuerpo:
- Los carbohidratos proporcionan energía.
- Las proteínas construyen y reparan tejidos.
- Las grasas apoyan la función celular y proporcionan energía duradera.
Las proporciones de estos macronutrientes en la dieta pueden variar según factores como la edad, el nivel de actividad, los objetivos de salud y las preferencias individuales.
Cálculo de la Ingesta de Macronutrientes: Las necesidades de macronutrientes varían de persona a persona. Calcular la ingesta de macronutrientes a menudo implica determinar la proporción óptima de carbohidratos, proteínas y grasas según los requisitos de energía y objetivos específicos, como el control de peso o el aumento de masa muscular.
Dieta Equilibrada: Una dieta equilibrada incluye una variedad de alimentos que proporcionan los macronutrientes necesarios en proporciones adecuadas. Las Pautas Dietéticas recomiendan que los carbohidratos representen alrededor del 45-65% de las calorías diarias totales, las proteínas alrededor del 10-35% y las grasas alrededor del 20-35%.
Personalización: Las necesidades de macronutrientes pueden diferir según factores como la edad, el género, el metabolismo y el nivel de actividad. Los atletas pueden requerir más proteínas para la reparación muscular, mientras que las personas que se centran en la pérdida de peso pueden necesitar ajustar su ingesta de carbohidratos.
En resumen, la macronutrición es la práctica de gestionar la ingesta de carbohidratos, proteínas y grasas para asegurar que el cuerpo reciba la energía y los nutrientes necesarios para un funcionamiento óptimo. Equilibrar estos macronutrientes juega un papel vital en lograr y mantener una buena salud.
Blog de educación para entrenadores personales Educación Escrito por Joe Antouri / CEO PROPTA. Todos los derechos reservados.
Instituto Mundial para la Educación y Certificación en Fitness y Nutrición.

